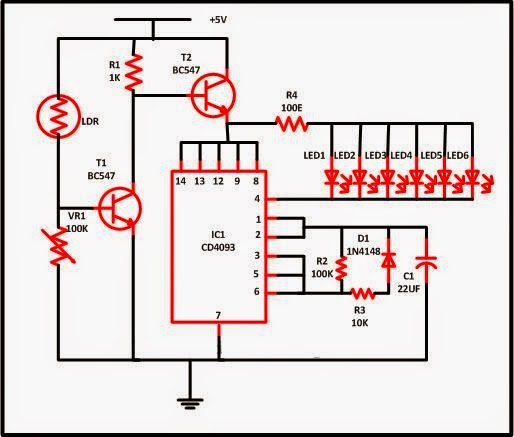
The MAX16834 is a neat little chip (it's not the only one, there are plenty of others out there) that allows high efficiency designs for LED string driving. It provides a platform for a Buck or Boost converter design, as well as brightness adjustment via analog/PWM input pins, as well as a fault output (in case of open/short circuits for example) and also diverse other functionalities that can be quite useful.